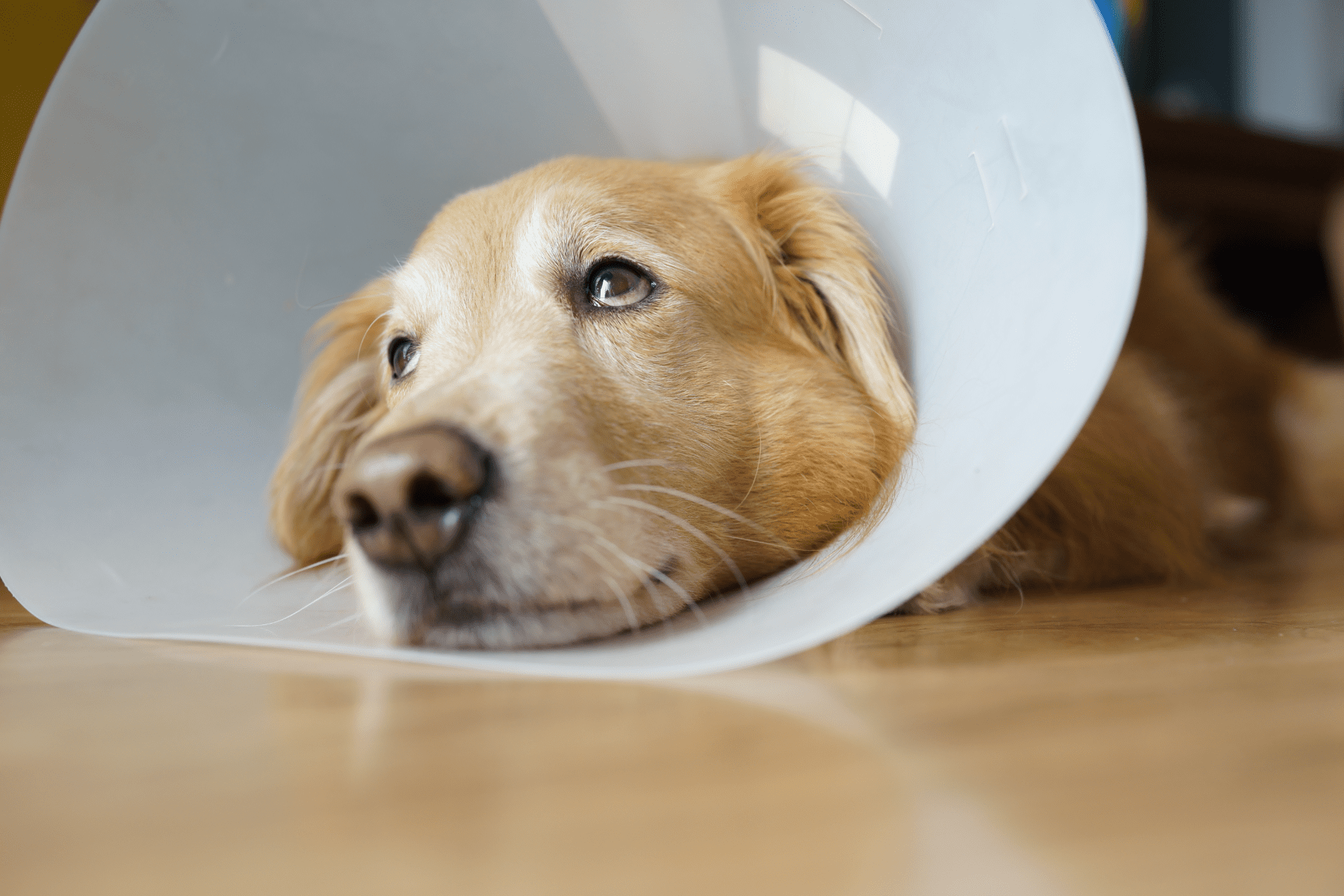
What is a Dog Cone?
A dog cone, commonly referred to as an “Elizabethan collar” or simply an “E-collar,” is a protective medical device that prevents dogs (or cats) from reaching wounds, surgical sites, injuries, or affected areas that need to heal. The design resembles a lampshade and extends outward from the neck, preventing the dog from biting, licking, or scratching their wounds or stitches.
Reasons for Using a Dog Cone:
- After Surgery: To prevent dogs from licking or chewing at surgical sites which can lead to infections or complications.
- Skin Conditions: To avoid further irritation from scratching or licking.
- Injuries: To protect wounds, bites, or other injuries from being aggravated.
Types:
- Plastic Cones: These are the traditional and most commonly seen E-collars. They are made of hard clear or colored plastic.
- Soft Cones: Made of padded nylon or similar materials, these are more comfortable and can be a good alternative for dogs who find hard cones distressing.
- Inflatable Cones: These resemble a travel pillow. They prevent the dog from turning its head to reach wounds but allow for more comfort when resting.
- Bite-Not Collar: Resembles a neck brace, restricts neck movement, and allows for better mobility and vision.
- DIY Cones: Some pet owners craft makeshift cones from materials like cardboard or towels in emergencies.
Tips:
- Proper Fit: Ensure the cone extends beyond the dog’s muzzle. If it’s too short, the dog may still be able to reach certain areas.
- Comfort: Make sure it’s snug enough not to slip off but not so tight that it’s choking your pet.
- Monitor Your Dog: Especially in the beginning, observe how your dog adjusts to the cone. Ensure they’re not getting stuck in tight spaces or injuring themselves further.
- Feeding and Drinking: Some dogs might find eating or drinking with the cone challenging. If this is the case with your dog, remove the cone during meals or use elevated bowls.
- Cleaning: Wounds can discharge fluids. Regularly clean the inside of the cone to avoid potential infections.
Alternatives to:
- Protective Clothing: There are protective suits and shirts available that can cover surgical sites or injuries.
- Taste Deterrents: Sprays with a bitter taste can deter some dogs from licking wounds. However, they might not be suitable for all wounds or dogs.
- Bandages: For some injuries or locations, a well-applied bandage might deter the dog enough.
Always consult a veterinarian regarding the best choice and duration for using an E-collar or alternative. While dogs often dislike wearing cones, it’s important to remember that their use is typically for the dog’s benefit, preventing complications that can arise from self-inflicted injuries or infections.